Bleeding Gums
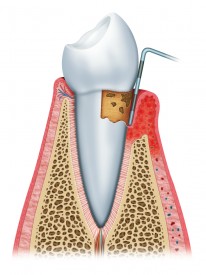
Tender, painful gums, or gum tissue that bleeds can make your mouth too sensitive to eat or even brush your teeth. Depending on the severity of the oral health condition, the diagnosis may be anything from gingivitis to severe gum disease.
What To Do
Actively bleeding gums and gums that are painful indicate that some type of infectious or disease condition is present. You will need to schedule an appointment with your dentist to determine the cause of the pain and bleeding. In most cases, your dentist will recommend a professional dental cleaning as well. This can remove tartar and bacteria along the gumlines that contribute to the condition.
Some ways to reverse bleeding and tender gums include:
- Regular preventive cleanings every 6 months
- Deep cleaning / periodontal therapy
- Brushing along the gumlines to prevent more buildup from forming
- Flossing under the gums between the teeth to remove plaque and bacteria
If only minor gingivitis is present, symptoms should typically be reversible within 2 weeks of dedicated brushing and flossing. Should symptoms persist, a more significant condition is present.
Potential Causes
In most cases, painful, bleeding gums are caused by periodontal disease (also known as “gum disease.”) This is due to an accumulation of tartar along the gumlines and under the gum tissue on the surfaces of the roots. The body’s response to the invasion of this bacterium is to attack it with antibodies that consequently also cause inflammation, bleeding, and destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth.
Swollen gums may also occur due to isolated infections like an abscessed tooth. If the swelling appears like a “pimple” on the surface of the gums, this is likely the underlying cause. An abscess on the gums means that the nerve tissue of the tooth has been damaged or infected.
Being anemic or on an aspirin regimen can slo make gum tissue bleed more than it ought to. However, it does not result in painful gum tissue.
Risks Of Not Treating
Active gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults. Pain and bleeding of the gums is typically one of the first symptoms that people notice. Other risks and symptoms associated with periodontal disease include:
- Bad breath caused by bacteria under the gumlines
- Gum recession and the appearance of “long” teeth
- Deep gum pockets caused by tissue detachment
- Loss of bone support around the teeth
- Mobility of teeth, or teeth that have fallen out
- Visible tartar buildup across the mouth
- The need for gum grafting treatments due to severe recession
- The need for bone implants or grafts due to loss of natural bone support
Allowing periodontal disease to go untreated will result in bone loss throughout the entire mouth. Not only does this lead to tooth loss, it can also make it difficult for tooth replacement treatments like dentures or implants to be held securely in the mouth.
Benefits Of Treating
Thankfully, gingivitis (the earliest form of gum disease) is completely reversible when treated in its beginning stages. Reversing the condition will prevent gum tissue from detaching or the loss of teeth caused by bone loss. A professional cleaning and oral hygiene consultation with your dental hygienist is one of the best ways to start out with a “blank slate” and get your gum tissue back to normal within a couple of weeks.
Moderate to severe periodontal disease should be treated by your dentist or hygienist. Professional deep cleanings remove calcified tartar from the tooth surface and create a clean environment that will encourage gum tissue to reattach to the tooth root. Because periodontal pockets can be extremely deep, regular flossing is not effective at cleaning the area or preventing buildup. Your hygienist will clean these areas thoroughly, putting you back on the road to successful oral health.
Alternative Treatments
Effective home oral hygiene will reduce mild gingivitis symptoms when performed properly. Brushing along the gumlines for a minimum of two minutes, twice each day is very important. Wrap floss tightly around each tooth and slide up and down under the gums several times, repeating the step along the sides of each tooth at least once a day. If symptoms do not reverse within 2 weeks, it’s time to seek professional care.
Your dentist may also prescribe a rinse to use, which limits the levels of bacteria in the mouth and improves healing after a professional periodontal treatment.
Depending on the severity of bone loss that has occurred, after a deep cleaning it may also be necessary to place a local antibiotic treatment in specific areas of infection. These small capsules deliver a constant dose of medication in areas of severe infection, increasing the response to professional therapy.
How long have your gums bled or been sore? Healthy gums don’t bleed and aren’t tender when you brush them. If symptoms have lasted for more than 2 weeks, schedule an appointment with your dentist today.


